What's On This Page?
ToggleIn the vast universe of our body’s cellular communication, one particular receptor might hold more significance than we ever imagined. It’s called the P2X7 receptor, and while it may not be a household name (yet), understanding its function could be a game-changer for managing anxiety and depression, as well as a spectrum of health conditions from mood disorders to chronic inflammation.
Today, let’s delve into the world of this powerful receptor, explore its potential impacts on health, and discuss how natural remedies might influence its activity.
What is the P2X7 Receptor?
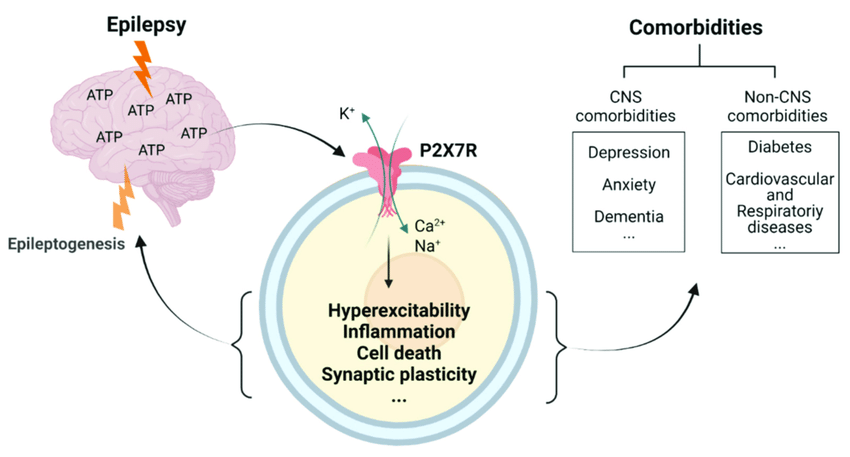
The P2X7 belongs to a broader group of P2X receptors. It’s a specific receptor found on the surface of certain cells, including immune and glial cells, which are crucial for brain function. The image above is excerpted Beyond Seizure Control: Treating Comorbidities in Epilepsy via Targeting of the P2X7 Receptor.
This receptor is unique because it responds to signals of cellular stress and damage by opening its channel when it binds with adenosine triphosphate (ATP), an energy molecule that juices up all of our cellular functions.
When ATP is found outside the cells in high concentrations, it means stress and cell damage. It’s not good. Remember, ATP is an energy molecule. The P2X7 receptor acts as a guardian, triggering immune responses and inflammation when issues like infections or tissue damage occur.
Let’s discuss the picture above. It’s basically showing how seizures and epilepsy result in high levels of ATP outside the cells in the brain. This excessive ATP activates P2X7 receptors. Once activated, these receptors contribute to cell death, inflammation, abnormal changes in how neurons connect and communicate, and alterations in neurotransmitter dynamics. It’s that last part that contributes to anxiety and depression too!
These biochemical changes lead to more seizures and other related health issues, indicating that the interaction between ATP and P2X7 receptors is a critical pathway linking brain ‘hyperactivity’ with the additional health complications seen in epilepsy. 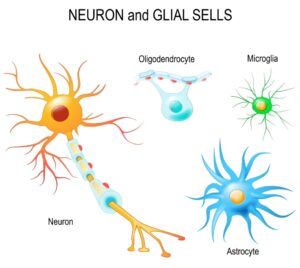
Where in the Body is the P2X7 Receptor Found?
The P2X7 receptor is not just located in one organ, or one part of the body, it’s all over:
- Immune Cells: Here, it modulates the release of cytokines, which are chemicals that can cause or reduce inflammation. Activation of these receptors will spawn pro-inflammatory cytokines (like IL-1β).
- Other Tissues: It’s also found in the skin, lungs, and gut, where it helps manage local immune responses.
- Brain (Glial Cells): It plays a crucial role in managing neuroinflammation, which can affect mood and pain perceptions. Glial cells, including astrocytes and oligodendrocytes, are involved in several processes that directly and indirectly affect mood. Astrocytes are like the brain’s sponges, soaking up excess neurotransmitters like glutamate and GABA right out of the gaps between neurons.This keeps our brain signals running smoothly, which directly influences how we feel and our overall mood. Astrocytes help maintain the blood-brain barrier. A compromised barrier can cause inflammation and neural dysfunction, which leads to depression. Oligodendrocytes (also a glial cell) are responsible for myelination of neurons in the central nervous system. Proper myelination is essential for the efficient transmission of electrical impulses across neurons.Dysmyelination has been linked to psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Overmyelination has been linked to misophonia, albeit it probably is not the cause. If you have this condition where you get unsettled, anxious or angry with certain sounds (like chewing, tapping, breathing, etc), you may be interested in my article that mentions myelin’s role, When Noise Triggers Rage: Exploring The Mysteries Of Misophonia.
The Role of P2X7 in Health and Disease
Understanding the P2X7 receptor is not just an academic exercise—it has real implications for health and disease management:
- Mental Health: Research suggests that overactivity of the P2X7 receptor in the brain might contribute to anxiety and depression due to its role in neuroinflammation.
- Inflammatory Diseases: Because it’s involved in inflammatory responses, this receptor is a potential target for treating autoimmune diseases and other chronic inflammatory conditions.
- Pain Management: P2X7 helps to signal pain, making it a target for developing new painkillers that are more effective and have fewer side effects than current options.
Managing Inflammation: To Block or Not to Block P2X7
To effectively manage inflammation, it is typically advisable to block the P2X7 receptor. That’s because, when activated this receptr significantly contributes to inflammation, which is bad for mental health concerns and chronic illness. So blocking P2X7 can prevent excessive inflammation by stopping the cascade of immune responses it triggers. This includes the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the promotion of cell death that can exacerbate inflammation and pain!
Can Natural Remedies Influence the P2X7 Receptor?
While most of the research on P2X7 targets pharmaceutical interventions, there’s growing interest in how natural substances might affect this pathway, specifically act as a P2x7 inhibitor. The answer is yes, and these 3 compounds come to mind:

- Caffeine: It affects the broader network of receptors, which includes P2X7, potentially modulating its activity indirectly through its effects on adenosine receptors. That coffee isn’t such a guilty pleasure if it’s helping P2X7.
- Curcumin and Resveratrol: These 2 natural compounds have shown promise in modulating inflammation, possibly impacting the P2X7 pathways. Dosages should be followed based upon the product you purchase, or what your physician tells you. Generally speaking, for cucurmin it’s somewhere between 500 and 2,000 mg per day (in divided doses, as tolerated). For resveratrol, it is something like 150 to 500 mg daily.
Curcumin and P2X7 Inhibition = Antidepressant Effects
Curcumin, a compound from turmeric, is noted for its anti-inflammatory properties and potential to treat depression, especially after a stroke. This condition, known as post-stroke depression, is linked to brain inflammation that can exacerbate depression.

In a STUDY where rats underwent a procedure simulating a stroke and then were subjected to stress to induce depression-like behaviors, curcumin was tested for its effectiveness. The results showed that curcumin not only reduced behaviors associated with depression but also decreased the accumulation of calcium and inflammation in the brain.
The study also evaluated how curcumin interacted with the P2X7 receptor. Blocking this receptor enhanced curcumin’s beneficial effects.
This suggests that curcumin’s ability to mitigate post-stroke depression symptoms might be largely due to its action on P2X7, pointing to some pretty valuable benefits in managing depression. The details are in Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.
I can’t resist telling you that I put one of the best brand of this herb into my Joint Script capsules which help with cytokine balance, flexibility and joint health.* It contains C3 Curcuminoids which you can read about HERE.
Implications for Other Health Conditions
The activity of the P2X7 receptor may also be linked to other major health conditions:
- Cholesterol and Heart Disease: Given its role in inflammation, P2X7 might negatively influence heart health, as chronic inflammation (and HOMOCYSTEINE) is a known risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.
- Asthma and Respiratory Conditions: Its expression in lung tissues suggests a potential role in inflammatory respiratory conditions like asthma. Read, Breathe Easy: Understanding Prescribed Asthma Medications.
- Thyroid Health: While direct connections between P2X7 and thyroid health are not well established, the receptor’s influence on overall immune health could indirectly affect thyroid function, particularly in autoimmune thyroid diseases. You may be interested in Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Help for the 5 Most Devastating Complications.
Practical Tips for Everyday Health
Understanding such a complex receptor might seem daunting, as well as boring. But over time there will be more research and information since it’s a gateway to inflammation associated with chronic illnesses. Here are a few practical ways to potentially modulate the activity of the P2X7 receptor for better health:
- Dietary Choices: Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric (curcumin) and grapes or berries (resveratrol) can be a simple way to support overall health.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Regular exercise and stress management techniques can help maintain optimal ATP levels and reduce unnecessary activation of the P2X7 receptor.
- Avoid Inflammatory Foods/Meds: The intake of chemicals and artificial ingredients, or other allergens may impact the gut which is where the immune cells are made. Limit or avoid them.
Summary
In summary, to control inflammation, particularly in chronic inflammatory and autoimmune conditions, the strategy is typically to block or inhibit the P2X7 receptor. This helps mitigate the inflammatory cascade triggered by its activation, offering relief from symptoms and potentially slowing the progression of inflammatory diseases. As always, any treatment strategy should be discussed with and managed by a healthcare provider to ensure it is appropriate for the individual’s specific health circumstances.

Suzy Cohen, has been a licensed pharmacist for over 30 years and believes the best approach to chronic illness is a combination of natural medicine and conventional. She founded her own dietary supplement company specializing in custom-formulas, some of which have patents. With a special focus on functional medicine, thyroid health and drug nutrient depletion, Suzy is the author of several related books including Thyroid Healthy, Drug Muggers, Diabetes Without Drugs, and a nationally syndicated column.



